Bring Learning to Life
Fueling Success: Wherever Learning Happens
Empower your teaching with digital tools and resources that provide impactful learning experiences and improve student outcomes, all designed to meet the dynamic needs of educators and learners.
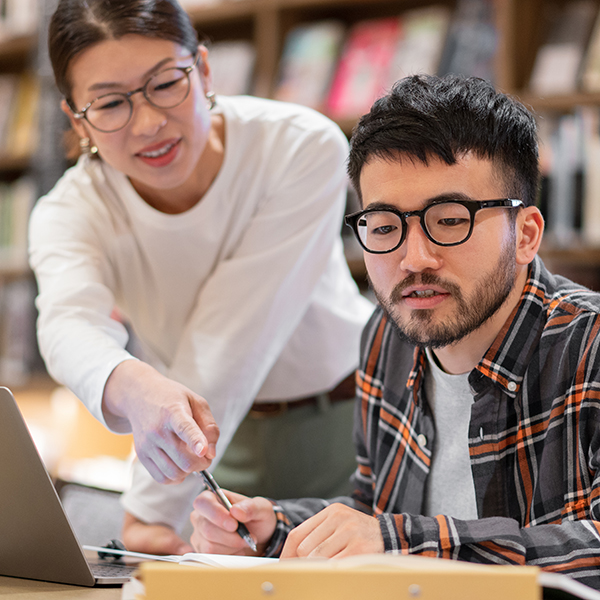

Instructors
Explore powerful instructor tools and resources for your discipline.

Students
Resources and tools to support your unique learning journey.
Achieve
Sign in or set up an Achieve account.
Academic integrity isn’t optional—it’s essential.
Achieve + Respondus Integration, Now Available
Strong assessments, now with more security. Pair quality assessments with the peace of mind of enhanced exam security.
Turn Your Class Into the Most Loved Course
Proven to improve course performance and student success in and out of the classroom by fostering reflective thinking and effective study strategies.
Improve Student Outcomes
LearningCurve's adaptive quizzing personalizes the learning experience, resulting in improved exam scores and grades, particularly for first-generation students.
Metacognitive Skills Development
Goal-setting and Reflection Surveys promote critical thinking and self-regulation, resulting in improved performance and final grades.
Foster Sense of Belonging
Achieve creates an inclusive environment that fosters engagement and motivation, leading to higher persistence and graduation rates.
Instructor Resources Hub
Easily access everything you need for your course in Achieve. From assessment questions and test banks to tailored teaching materials, Achieve houses the best resources to support your teaching.
A dynamic, all-in-one active learning tool that improves learning outcomes through collaboration and active participation.
Improve Classroom Engagement
Instant polling and group work encourage students to share opinions and assess knowledge in real time.
Promote Critical Thinking
Peer discussions and group activities promote analysis, debate, and reflection, resulting in a deeper understanding of topics.
Foster Accountability
Automated attendance and in-class quizzes establish clear expectations, fostering accountability and ownership of learning.
Simplify Classroom Management
Easily organize activities, monitor progress, and implement active learning strategies, all from one platform.
The Impact of Learning Science
Empower student success with evidence-based product experiences
See the ResearchAI Tools to Help You Work Smarter, Not Harder
Harness AI to foster meaningful learning experiences without losing the human connection, freeing you to focus on what matters most: inspiring student success.
Generate Unique Questions
Use iClicker’s AI Question Creator to save time and assess student understanding with tailored questions aligned to your teaching style and course content.
Personalized Homework Support
Achieve’s AI Student Tutor uses a Socratic approach to guide students through thoughtful questions and instant, tailored feedback.
Professional Development Courses
Take your teaching to the next level with professional development courses and peer learning community.
Ensure Student Privacy
We respect student privacy rights. Learn more about Macmillan Learning’s AI policies.