Page 35 - 2024-calc4e-SE proofs-4e.indd
P. 35
Sullivan 04 apcalc4e 45342 ch02 166 233 5pp August 7, 2023 12:54
Section 2.2 • The Derivative as a Function; Differentiability 185
Since f is differentiable at c, we know that
f (x) − f (c)
lim = f (c)
′
x→c x − c
is a number. Also for any real number c, lim(x − c) = 0. So
x→c
h i
lim[ f (x) − f (c)] = [ f (c)] lim(x − c) = f (c) · 0 = 0
′
′
© 2024 BFW Publishers PAGES NOT FINAL - For Review Purposes Only - Do Not Copy.
x→c x→c
That is, lim f (x) = f (c), so f is continuous at c.
x→c
An equivalent statement of this theorem gives a condition under which a function
has no derivative.
COROLLARY
If a function f is discontinuous at a number c, then f is not differentiable at c.
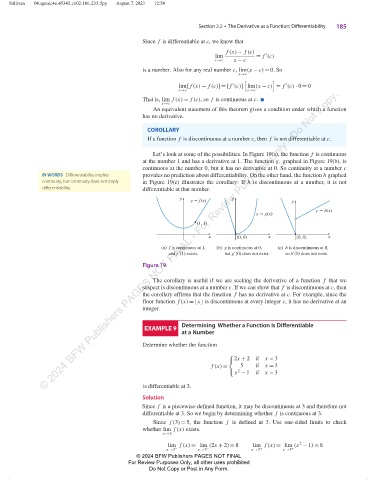
Let’s look at some of the possibilities. In Figure 19(a), the function f is continuous
at the number 1 and has a derivative at 1. The function g, graphed in Figure 19(b), is
continuous at the number 0, but it has no derivative at 0. So continuity at a number c
IN WORDS Differentiability implies provides no prediction about differentiability. On the other hand, the function h graphed
continuity, but continuity does not imply in Figure 19(c) illustrates the corollary: If h is discontinuous at a number, it is not
differentiability. differentiable at that number.
y y f (x) y y
y h(x)
y g(x)
(1, 1)
x (0, 0) x (0, 0) x
(a) f is continuous at 1, (b) g is continuous at 0, (c) h is discontinuous at 0,
and f (1) exists. but g (0) does not exist. so h (0) does not exist.
Figure 19
The corollary is useful if we are seeking the derivative of a function f that we
suspect is discontinuous at a number c. If we can show that f is discontinuous at c, then
the corollary affirms that the function f has no derivative at c. For example, since the
floor function f (x) = ⌊x⌋ is discontinuous at every integer c, it has no derivative at an
integer.
Determining Whether a Function Is Differentiable
EXAMPLE 9
at a Number
Determine whether the function
2x + 2 if x < 3
5 if x = 3
f (x) =
2
x − 1 if x > 3
is differentiable at 3.
Solution
Since f is a piecewise-defined function, it may be discontinuous at 3 and therefore not
differentiable at 3. So we begin by determining whether f is continuous at 3.
Since f (3) = 5, the function f is defined at 3. Use one-sided limits to check
whether lim f (x) exists.
x→3
2
lim f (x) = lim (2x + 2) = 8 lim f (x) = lim (x − 1) = 8
x→3 − x→3 − x→3 + x→3 +
© 2024 BFW Publishers PAGES NOT FINAL
For Review Purposes Only, all other uses prohibited
Do Not Copy or Post in Any Form.