Page 30 - 2024-calc4e-SE proofs-4e.indd
P. 30
Sullivan 04 apcalc4e 45342 ch02 166 233 5pp August 7, 2023 12:54
180 Chapter 2 • The Derivative and Its Properties
EXAMPLE 1 Finding the Derivative Function
2
Find the derivative of the function f (x) = x − 5x at any real number x using Form (2).
Solution
Using Form (2), we have
Figure 8 © 2024 BFW Publishers PAGES NOT FINAL - For Review Purposes Only - Do Not Copy.
2
2
f (x + h) − f (x) [(x + h) − 5(x + h)] − (x − 5x)
′
f (x) = lim = lim
h→0 h h→0 h
2
2
2
2
[(x + 2xh + h )− 5x − 5h] − x + 5x 2xh + h − 5h
= lim = lim
h→0 h h→0 h
h(2x + h − 5)
= lim = lim(2x + h − 5) = 2x − 5
h→0 h h→0
R
NOW WORK AP Practice Problem 2.
The domain of the function f is the set of real numbers in the domain of f for
′
which the limit expressed in Form (2) exists. So the domain of f is a subset of the
′
domain of f .
We can use either Form (1) or Form (2) to find derivatives using the definition.
However, if we want the derivative of f at a specified number c, we usually use
Form (1) to find f (c). If we want to find the derivative function of f , we usually use
′
Form (2) to find f (x). In this section, we use the definitions of the derivative,
′
Forms (1) and (2), to investigate derivatives. In the next section, we begin to develop
formulas for finding the derivatives.
EXAMPLE 2 Finding the Derivative Function
√
NOTE The instruction “differentiate f ” Differentiate f (x) = x and determine the domain of f .
′
means “find the derivative of f .”
Solution
The domain of f is {x|x ≥ 0}. To find the derivative of f, we use Form (2). Then
√ √
f (x + h) − f (x) x + h − x
f (x) = lim = lim
′
h→0 h h→0 h
Rationalize the numerator to find the limit.
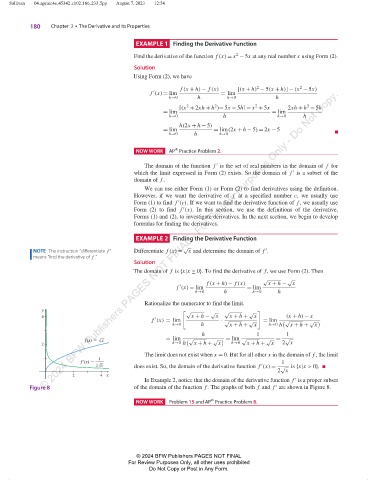
y " √ √ √ √ #
4 x + h − x x + h + x (x + h) − x
f (x) = lim · √ √ = lim √ √
′
h→0 h x + h + x h→0 h x + h + x
h 1 1
= lim √ √ = lim √ √ = √
f(x) x
2 h→0 h x + h + x h→0 x + h + x 2 x
The limit does not exist when x = 0. But for all other x in the domain of f , the limit
1
f'(x) 1
2 x does exist. So, the domain of the derivative function f (x) = √ is {x|x > 0}.
′
2 x
2 4 x
′
In Example 2, notice that the domain of the derivative function f is a proper subset
′
of the domain of the function f . The graphs of both f and f are shown in Figure 8.
R
NOW WORK Problem 15 and AP Practice Problem 8.
© 2024 BFW Publishers PAGES NOT FINAL
For Review Purposes Only, all other uses prohibited
Do Not Copy or Post in Any Form.