Page 66 - 2024-bfw-starnes-TPS7e-SE proofs.indd
P. 66
SecTIoN 1D Describing Quantitative Data with Numbers 53
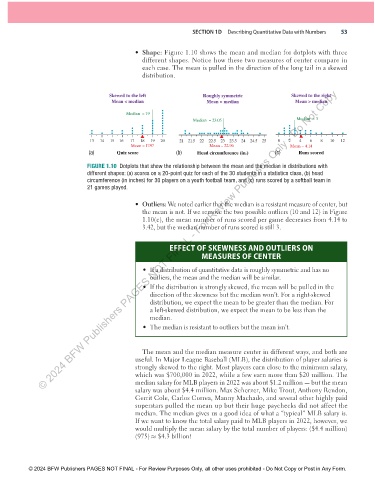
• Shape: Figure 1.10 shows the mean and median for dotplots with three
different shapes. Notice how these two measures of center compare in
each case. The mean is pulled in the direction of the long tail in a skewed
distribution.
2- Do Not Copy
Skewed to the left Roughly symmetric Skewed to the right
Mean < median Mean ≈ median Mean > median
Median = 19
Median = 23.05 Median = 3
© 2024 BFW Publishers PAGES NOT FINAL - For Review Purposes Only
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 21.5 22 22.5 23 23.5 24 24.5 25 0 4 6 8 10 12
Mean = 17.97 Mean = 22.96 Mean = 4.14
(a) Quiz score (b) Head circumference (in.) (c) Runs scored
FIGURE 1.10 Dotplots that show the relationship between the mean and the median in distributions with
different shapes: (a) scores on a 20-point quiz for each of the 30 students in a statistics class, (b) head
circumference (in inches) for 30 players on a youth football team, and (c) runs scored by a softball team in
21 games played.
• Outliers: We noted earlier that the median is a resistant measure of center, but
the mean is not. If we remove the two possible outliers (10 and 12) in Figure
1.10(c), the mean number of runs scored per game decreases from 4.14 to
3.42, but the median number of runs scored is still 3.
EFFECT OF SKEWNESS AND OUTLIERS ON
MEASURES OF CENTER
• If a distribution of quantitative data is roughly symmetric and has no
outliers, the mean and the median will be similar.
• If the distribution is strongly skewed, the mean will be pulled in the
direction of the skewness but the median won’t. For a right-skewed
distribution, we expect the mean to be greater than the median. For
a left-skewed distribution, we expect the mean to be less than the
median.
• The median is resistant to outliers but the mean isn’t.
The mean and the median measure center in different ways, and both are
useful. In Major League Baseball (MLB), the distribution of player salaries is
strongly skewed to the right. Most players earn close to the minimum salary,
which was $700,000 in 2022, while a few earn more than $20 million. The
median salary for MLB players in 2022 was about $1.2 million — but the mean
salary was about $4.4 million. Max Scherzer, Mike Trout, Anthony Rendon,
Gerrit Cole, Carlos Correa, Manny Machado, and several other highly paid
superstars pulled the mean up but their huge paychecks did not affect the
median. The median gives us a good idea of what a “typical” MLB salary is.
If we want to know the total salary paid to MLB players in 2022, however, we
would multiply the mean salary by the total number of players: ($4.4 million)
(975) ≈ $4.3 billion!
© 2024 BFW Publishers PAGES NOT FINAL - For Review Purposes Only, all other uses prohibited - Do Not Copy or Post in Any Form.
02_StarnesTPS7e_40934_un01_p1_001_086_6pp.indd 53 13/09/23 5:38 PM